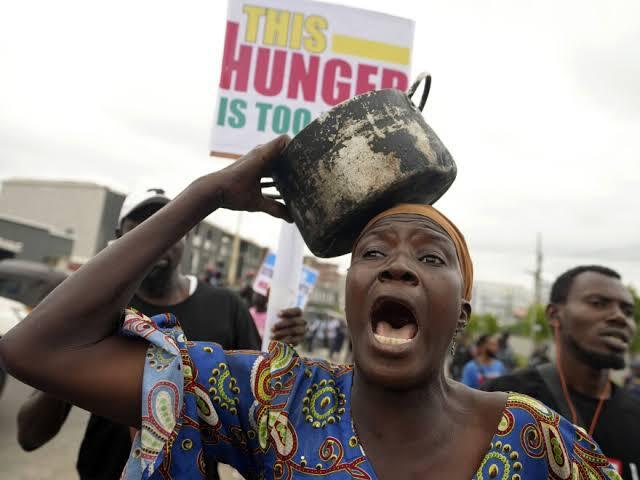The United Nations World Food Programme (WFP) has issued a stark warning regarding an escalating hunger crisis affecting millions in West and Central Africa. The region is grappling with unprecedented levels of food insecurity driven by conflict, displacement, economic challenges, and extreme weather events.
Recent analyses indicate that approximately 36 million people are currently unable to secure their basic food needs, a figure expected to exceed 52 million during the critical lean season from June to August. Among those affected, nearly three million individuals are experiencing emergency conditions, with 2,600 individuals in Mali facing the threat of catastrophic hunger.
Despite the alarming rise in food insecurity, resources remain critically limited, placing millions at risk. Margot van der Velden, Regional Director for West and Central Africa, emphasized, “Without immediate funding, WFP will be compelled to further reduce both the number of individuals assisted and the size of food rations provided.”
In comparison to 2019, when only four percent of the population faced food insecurity, the current figure has surged to 30 percent, according to Ollo Sib, a senior research adviser at WFP. He expressed hope that the urgency of the situation in the Sahel would capture the attention it deserves during a press conference in Geneva from Dakar.
Sib recently visited some of the hardest-hit areas, including northern Ghana, where communities are dealing with severe drought conditions. “They have had to replant two to three times, and each failed sowing exacerbates their financial strain due to the high costs of fertilizers and seeds,” he noted.
The assessment team also traveled to northern Mali, the only region where catastrophic food security conditions are reported. Sib recounted conversations with pastoralist elders who typically sell livestock to purchase cereals but are now facing a 50 percent increase in food prices compared to the five-year average, all while struggling to access markets.
WFP highlighted that ongoing conflict is a key driver of the worsening hunger situation in West and Central Africa. More than 10 million vulnerable individuals have been displaced due to violence, including over two million refugees and asylum seekers in Chad, Cameroon, Mauritania, and Niger, with an additional eight million internally displaced, particularly in Nigeria and Cameroon.
Rising food and fuel costs have compounded the problem, leading to soaring levels of hunger. Furthermore, recurrent extreme weather events continue to undermine families’ ability to provide for themselves.
WFP is prepared to enhance its response and vital assistance efforts in West Africa and the Sahel, seeking $710 million to support life-saving operations until the end of October. Their goal is to assist nearly 12 million individuals this year, with three million already reached, including refugees, internally displaced persons, and vulnerable children and women.
However, the agency warns that five million people are at risk of losing access to assistance unless urgent funding is secured. WFP has also urged governments and partners to invest in sustainable solutions that strengthen resilience and reduce long-term reliance on aid.
Since 2018, WFP has collaborated with regional governments to tackle the root causes of hunger, successfully rehabilitating over 300,000 hectares of land to benefit more than four million people across 3,400 villages. (NAN)